With one of the youngest populations, a median age of 28, India can harness its demographic dividend by nurturing a workforce that is equipped with employable skills and prepared for the needs of the industry. Sixty-five per cent of India’s fast-growing population is under 35, and many lack the skills needed by a modern economy. However, it must be noted that the percentage has improved from around 34 per cent to 51.3 per cent in the last decade. The Indian government has been actively working to enhance skilling and employment opportunities across the nation, recognizing the pivotal role of human capital in driving economic growth and innovation. The document highlights such efforts in detail.
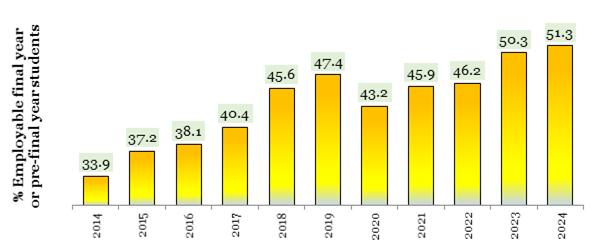
Source: India Skills Report, Wheebox
The 2022-23 Annual Report of the Ministry of Skill Development & Entrepreneurship (MSDE) underscores the challenges in this sector, emphasizing the need for comprehensive improvements in the skilling and entrepreneurship ecosystem within the country.
The recent launch of the Skill India Digital platform aimed at achieving skilling, education, employment, and entrepreneurship ecosystem marks another step towards the “ease of acquiring skill” in India. The rise in the number of candidates undergoing skill development through the Government’s flagship programmes has underlined the thrust to ‘Skill India’. The across-the-board progress in skilling has manifested in India’s rising position in WorldSkills Competitions, held every two years.
Graph: India at WorldSkills Competition
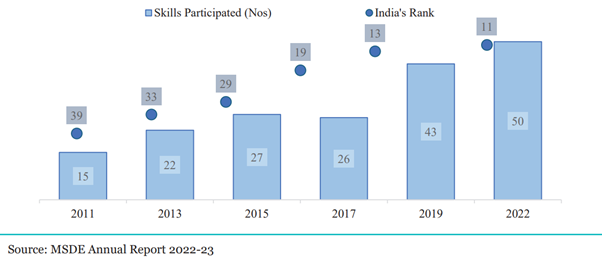
This sets the stage to discuss various government schemes and initiatives aimed at bolstering skill development and bridging the employability gap among India’s burgeoning young population.

Focus on Employment and Skilling in Budget 2024
Under the Union Budget 2024-25, a notable highlight was the announcement of a new centrally sponsored scheme under the Prime Minister’s package, in collaboration with state governments and industry. This scheme aims to skill 20 lakh youth over five years and upgrade 1,000 Industrial Training Institutes (ITIs).
Additionally, the announcement was made to revise the Model Skill Loan Scheme to facilitate loans up to ₹7.5 lakh with government-backed guarantees, which will benefit 25,000 students annually. For those ineligibles for existing schemes, financial support for loans up to ₹10 lakh for higher education in domestic institutions will be provided, with e-vouchers offering annual interest subvention of 3% for 1 lakh students each year.
This revised Model Skill Loan scheme was launched by Hon’ble Minister of State (I/C), Ministry of Skill Development and Entrepreneurship (MSDE), Shri Jayant Chaudhary on 25th July, 2024.
Government’s Skill Development Initiatives
National Policy on Skill Development & Entrepreneurship (NPSDE)
The NPSDE focuses on bridging gaps, improving industry engagement, establishing a quality assurance framework, leveraging technology, and expanding apprenticeship opportunities. Prioritising equity, it targets marginalised groups and emphasises skill development and entrepreneurship for women. In the entrepreneurial domain, the policy educates potential entrepreneurs, facilitates mentorship, fosters innovation, enhances ease of doing business, and promotes social entrepreneurship. This, in combination with the National Education Policy (NEP), holds tremendous potential for bridging the education-employment gap in India.

Pradhan Mantri Kaushal Vikas Yojana
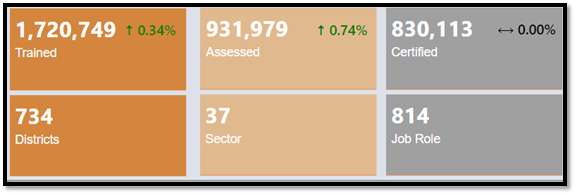
Since its inception in 2015, PMKVY has emerged as a cornerstone initiative in India’s skill development landscape. To date, the scheme has successfully trained 1.42 crore individuals, with 1.13 crore received certification across its Short-Term Training (STT), Special Projects (SP), and Recognition of Prior Learning (RPL) components. Over 1,000 educational institutions across the nation have been integrated as Skill India Centres, bolstering accessibility to skill enhancement opportunities. PMKVY has also been instrumental in introducing 119 new age and future skill courses spanning eight key sectors, ensuring alignment with evolving industry demands. One of PMKVY’s notable achievements lies in its focus on gender inclusivity, evidenced by a significant rise in female participation. The proportion of women trained under the scheme has increased commendably, from 42.7% in FY16 to 52.3% in FY24.
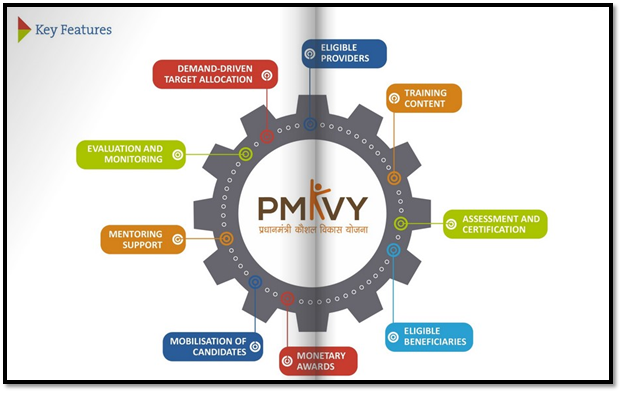
PMKVY PROGRESS
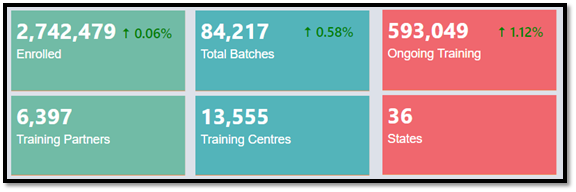
Craftsmen Training Scheme (CTS)
The Craftsmen Training Scheme (CTS) plays a crucial role in vocational training across India, facilitated through a vast network of 14,955 Industrial Training Institutes (ITIs). Particularly noteworthy is the increasing participation of women in long-term skilling programs within ITIs and National Skill Training Institutes (NSTIs), rising from 9.8% in FY16 to 13.3% in FY24. In addition to expanding access and enhancing participation, the Craftsmen Training Scheme has implemented a new Grading Mechanism for it is, known as the Data-driven Grading Methodology (DDGM), which utilizes parameters/information available on the NCVT MIS portal. Introduced from the session 2023-24 onwards, DDGM aims to standardize evaluation processes across it is.
Jan Shikshan Sansthan (JSS)
Jan Shikshan Sansthan (JSS) plays a pivotal role in imparting skills to non/neo literates and individuals with a rudimentary level of education. From FY19 to FY24, JSS has successfully trained 26.36 lakh individuals, with 24.94 been certified. Further, to enhance its effectiveness, JSS has initiated capacity building measures, including the setting up of 30 Model JSS by upgrading laboratories with new-age equipment and training 150 trainers. JSS has prioritized the professional development of its staff, focusing on enhancing management capabilities and communication skills. These efforts aim to modernize facilities and improve training methodologies to better serve the evolving needs of learners. Notably, JSS has demonstrated a strong commitment to gender equality, with women comprising approximately 82% of the total beneficiaries
National Apprenticeship Promotion Scheme (NAPS)
The National Apprenticeship Promotion Scheme (NAPS) is aimed at fostering apprenticeship training across India. Since its inception, a total of 32.38 lakh apprentices have been engaged in various sectors. The NAPS portal has witnessed significant growth, with the number of registered establishments increasing from 17,608 in March 2017 to 2.21 lakh by March 2024, highlighting widespread industry participation and support. The participation of women has notably increased from 7.74% in 2016-17 to 20.77% in 2023-24, reflecting efforts to encourage more women to pursue careers in diverse sectors. Furthermore, the scheme utilizes Direct Benefit Transfer (DBT) mechanisms under NAPS-2, facilitating the reimbursement of 25% of the apprentices’ stipend (up to ₹1,500) directly into their bank accounts. As of March 2024, a total of ₹320.88 crore has been disbursed through 22.46 lakh transactions, ensuring timely financial support to apprentices and encouraging more establishments to participate actively in the program.
Entrepreneurship Training
Entrepreneurship training in India has been significantly bolstered by institutions like the National Institute for Entrepreneurship and Small Business Development (NIESBUD) and the Indian Institute of Entrepreneurship (IIE). From FY19 to FY24, NIESBUD alone has provided essential entrepreneurial training to 3.21 lakh beneficiaries. Similarly, IIE Guwahati has extended training and handholding services to 1.43 lakh individuals during the same period, fostering a supportive environment for budding entrepreneurs across various sectors.
Skill India Digital Hub platform
The Skill India Digital Hub platform, launched in August 2023, represents a convergence platform facilitating access to skilling, credit, and employment through AI/ ML technology. This initiative integrates a comprehensive array of skilling schemes along with 690 online courses and 1650 QP-based e-books, enhancing accessibility to educational resources essential for vocational training. Furthermore, the platform seamlessly incorporates various government initiatives and services such as eShram/EPFO/NCS, Udyam, DigiLocker, GatiShakti, UMANG, AgriStack, PLI Schemes, and ODOP, etc. Since its inception, the Skill India Digital Hub has garnered significant engagement, with over 60 lakh learners registered and 8.4 lakh app downloads.

Beyond the initiatives led by the Ministry of Skill Development and Entrepreneurship (MSDE), India has embarked on targeted skilling efforts across diverse sectors. Under the Jal Jeevan Mission, MSDE provides overall guidance for a multi-skilling course. Similarly, the PM Vishwakarma initiative focuses on both basic and advanced skill training for Vishwakarmas, incorporating modern toolkits. The Green Hydrogen sector sees the development of 50 new short-term qualifications for skilling, upskilling, and re-skilling. Furthermore, PM-JANMAN spearheads entrepreneurship and skill development among Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Groups (PVTGs), with NIESBUD and IIE conducting capacity-building programs. By March 2024, these efforts have already benefited 5,096 beneficiaries, with plans to reach 44,608 by 2025-26. Additionally, special skill provisions for Agniveers through MoUs with the Army, Navy, and Airforce ensure skill certification based on qualifications and experiential learning, facilitating post-service employment opportunities across various industries.
Latest Achievements
Some of the key achievements/ initiatives by this Ministry during the month of July, 2024 are as under:
1. Skill Loan Scheme: The Hon’ble Minister of State (I/C), Ministry of Skill Development and Entrepreneurship (MSDE), Shri Jayant Chaudhary launched the revised Model Skill Loan Scheme on 25th July, 2024 with the objective of providing easy access to advanced-level skill courses, which potentially pose a significant financial barrier for many deserving students and candidates to gain futuristic and in-demand industry skills. Under the new Model Skill Loan Scheme, the maximum eligible loan amount has been increased from Rs. 1.5 lakh to Rs. 7.5 lakh.
2. World Youth Skills Day: The Hon’ble Minister of State (I/C), MSDE, Shri Jayant Chaudhary, attended an open house, “Kaushal Samwaad”, to celebrate World Youth Skills Day, which is recognised globally by the United Nations. The day also commemorated the 10th year celebrations of the Skill India Mission.
3. Apprenticeship Training Status: The apprentices engaged during the current financial year 2024-25 stand at 2,77,036 as of 31st July 2024. The total number of apprentices undergoing training as of 31st July 2024 stands at 7.46 lakh. The total number of establishments engaging/engaged apprentices till 31st July 2024 stands at 47,311.
4. DBT Status: The number of apprentices participating through DBT is increasing steadily and there is an increase from July 2023 (1,72,537) till July 2024 (5,49,812). During the period (April to July), GoI share of stipend amounting to Rs 122.36 Crore has been disbursed to apprentices through DBT.
Skilling India at Global Standards
India’s efforts in skilling at global standards are reflected through strategic initiatives such as the Skill India International Centers (SIIC) and partnerships facilitated through Government-to-Government (G2G) Memorandums of Understanding (MoUs). The establishment of 30 SIICs, as announced in the FY24 interim budget, marks a significant step towards enhancing India’s global skilling footprint. Currently operational centers in Varanasi and SDI Bhubaneswar exemplify this initiative’s early success, with plans finalized for seven more centers in the first phase.
Additionally, India has forged MoUs with prominent countries including Australia, Denmark, France, Germany, Japan, Qatar, UAE, and the UK for cooperation in Information Exchange, Standard Setting, Mutual Recognition of Qualifications, etc. Such partnerships not only enhance the international mobility but also promote the recognition of Indian qualifications abroad. Moreover, the establishment of NSDC International Limited in 2021, for ethical and transparent international recruitment of skilled Indians, drives the Skill India International Mission with a focus on priority sectors such as Information Technology, Construction, and Hospitality. Efforts include capacity building through 20 NSDC-affiliated training centers and language training at 12 centers, contributing to the deployment of over 26,000 skilled candidates across multiple countries.
Partnering with Industry for Skilling
Industry connection is crucial to any large-scale skilling programme, enabling contemporary relevance and employability and ascertaining demand to absorb the newly skilled workforce. In cognisance of this, the Skill India mission actively collaborates with the industry through National Skill Development Council (NSDC)-driven partnerships for skill development, reskilling, and upskilling. Until March 2024 (starting date to be added), 131 projects have been undertaken by NSDC, with 62 corporate organisations benefitting over 3.10 lakh persons across the country, including 42 aspirational districts.
Launched in 2021, the Skill Impact Bond leverages an innovative and results-based finance mechanism – Development Impact Bond99 model to attract private sector funds and expertise for skill development, job placements, and retention. This initiative by NSDC and its coalition partners100 targets training 50,000 youth, ensuring at least 60 per cent are female, through selected and monitored NSDC-affiliated training partners over four years. Between November 2021 and March 2024, 29,365 candidates have been enrolled over five cohorts, 23,464 have been certified, 19,209 have been placed and 13,853 reported job retentions. The program has reported 74 per cent women enrolment so far.
Further, the Directorate General of Training (DGT) has initiated several impactful collaborations under its Industry Partnerships framework, enhancing vocational training and industry readiness across diverse sectors. Through the Flexi MoU Scheme with prominent industry partners like Maruti Suzuki India Limited, NMDC Chhattisgarh, and Toyota Kirloskar Motor Pvt. Ltd., approximately 9,600 trainees have been trained since March 2019. The Dual System of Training (DST) provided firsthand workplace experience to over 37,865 trainees from 978 ITIs during the 2022 session. Collaborations with tech giants including IBM, Microsoft, Cisco, Adobe, and Amazon Web Services have prepared more than 21.5 lakh trainees for Industry 4.0 between November 2019 and March 2024. Additionally, NSTIs have conducted skilling initiatives with ISRO, ONGC, Indian Railways, Naval Ship Repair Yard, Naval Ship Dockyard, and BHEL, training about 1,400 participants in FY24. DGT continues to upgrade NSTIs/ITIs infrastructure with partners like Dassault, Pidilite, Jaguar, Skoda, HAL, and Siemens, ensuring industry-relevant skills development across sectors.
Conclusion
In conclusion, while India faces significant challenges with its skill gap, the government’s proactive initiatives have demonstrated tangible progress towards bridging this divide. Programs like Pradhan Mantri Kaushal Vikas Yojana, Craftsmen Training Scheme, and National Apprenticeship Promotion Scheme have collectively trained millions, fostering inclusivity and empowering women in traditionally underrepresented sectors. The launch of the Skill India Digital Hub and establishment of Skill India International Centers further illustrate India’s commitment to leveraging technology and global partnerships for skill enhancement at par with international standards. These efforts not only address current talent shortages across industries but also prepare India’s youth for the demands of a rapidly evolving global economy. Moving forward, sustained investment and collaboration between government, industry, and educational institutions will be crucial to ensuring that every young Indian has access to quality skill development opportunities, thus realizing the full potential of India’s demographic dividend.
Reference:
- https://www.indiabudget.gov.in/economicsurvey/
- https://pib.gov.in/PressReleaseIframePage.aspx?PRID=2035609#:~:text=Budget%20Estimates%202024%2D25%3A,receipt%3A%20%6025.83%20lakh%20crore
- https://pib.gov.in/PressReleaseIframePage.aspx?PRID=2035618
- https://www.indiabudget.gov.in/doc/budget_speech.pdf
- Monthly Summary for the month of July, 2024: https://www.skilldevelopment.gov.in/index.php/en/reports-documents/monthly-summary
Santosh Kumar/Sarla Meena
You may also like
-
India Drives AI Integration in Education to Build Talent Pipeline for Global Leadership
-
Civil Aviation Ministry Monitors Middle East Airspace Disruptions; Relief Flights Planned for Stranded Passengers
-
CCS Reviews West Asia Crisis; Focus on Safety of Indian Nationals and Regional Stability
-
Unique Identification Authority of India Partners with Google to Display Authorised Aadhaar Centres on Maps
-
Why India Refuses to Choose Sides : India’s Chanakyan Approach to World Politics
